BTree
This is the common data structure when DB store index.
- Each node has key - value
- Each node is a page
- N = M - 1
N: the number of element in a node
M: the number of children nodes
Limitation of BTree
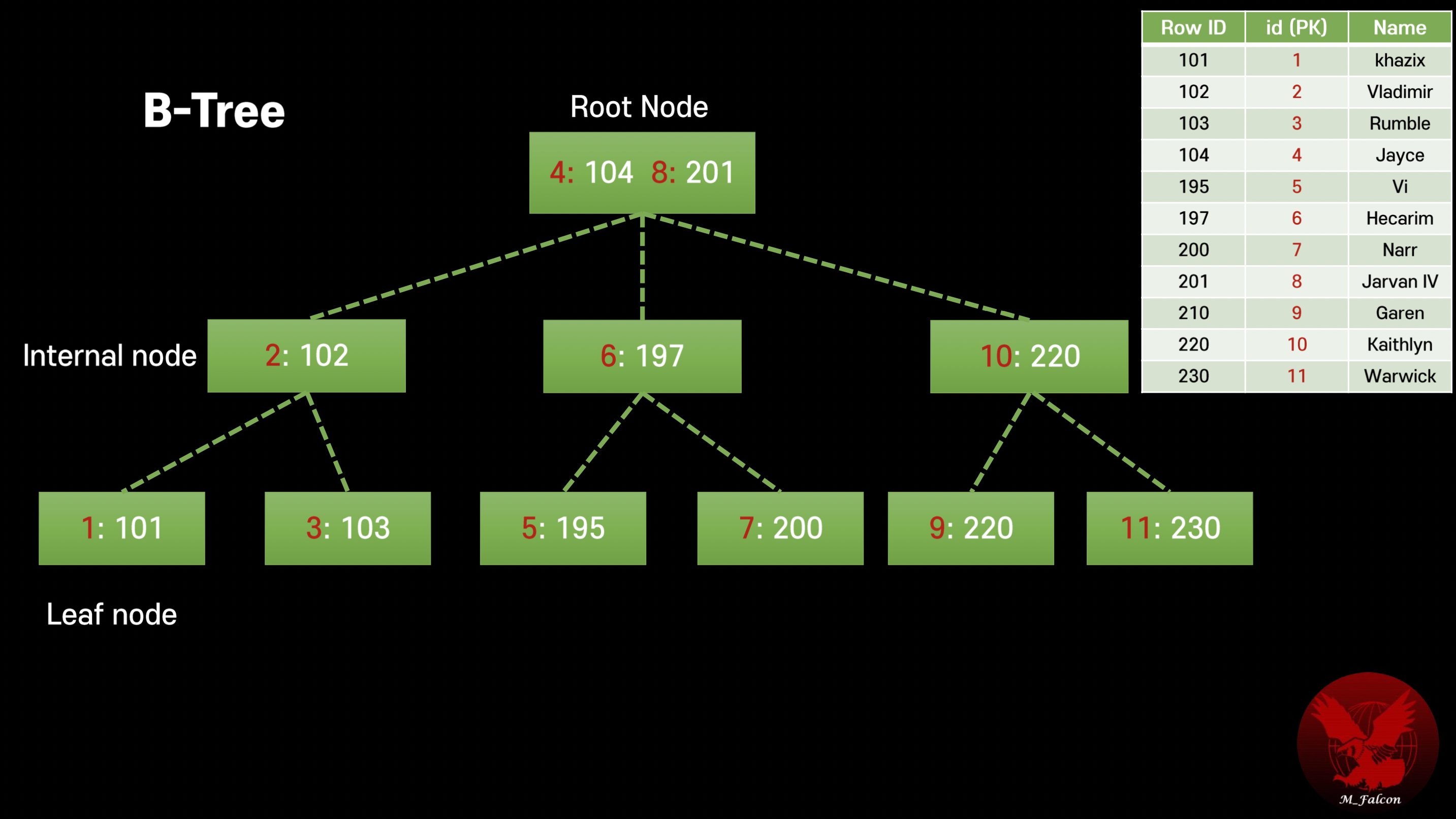
- Require more space since it has key (PK) : value (RowID)
👉🏻 more nodes == more page == more IO required => ⚠️ Make slower! - Range based queries are slow because of random access
There’s a lot of disk I/O jump even though PKs are sorted.
This limitation is the reason the B+Tree appears
B+Tree
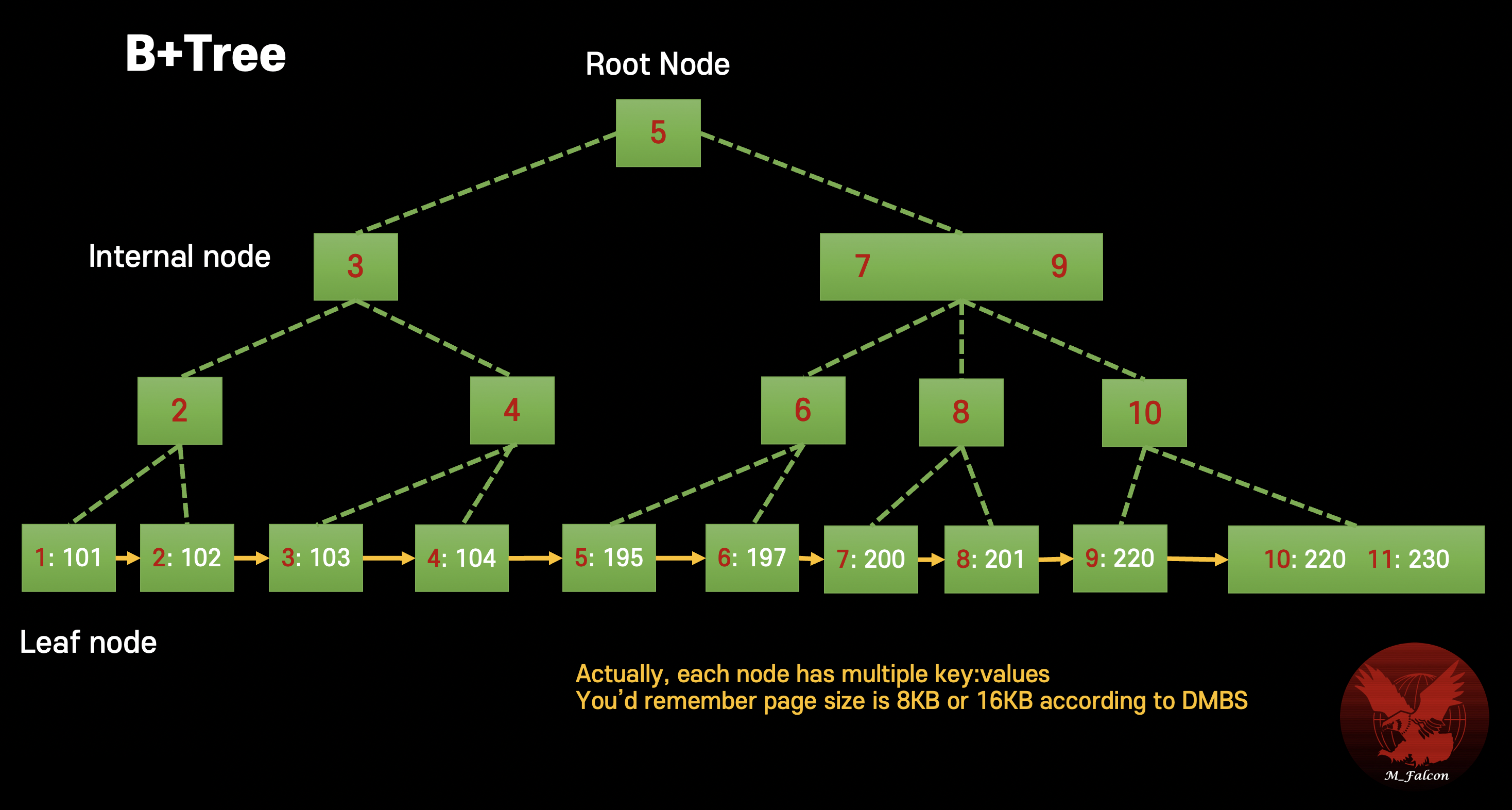
Actually, each node has multiple key-values. you’d remember the page size is 8KB or 16KB that is different according to DBMS.
What’s difference?
- Each root, internal nodes have only keys.
👉🏻 more elements => lower pages => lower I/O => Faster! - Each leaf node has key-value
value is a pointer to row (Row ID) - Leaf nodes are linked Once a leaf node is found, there is no need to check from the tree root
👉🏻 This makes range-based query faster.
Efficient range-based query

Check points in B+Tree
- Most DBMS use B+Tree
even MongoDB - Indexes are located and fit in In-memory
- Leaf nodes can live in data files in the heap.
- Leaf nodes are linked, and the cost of linking is cheap.
