Primary key
Organized, clustered table. we call it Index Organized Table (IOT)
Clustered index that is sequential is not that bad. So, it’s ordered data and can use efficient caching mechanism.
If not, memory in heap would jump left and right, That will not benefit of memory caching DB is doing.
Secondary Key
This is used in non-clustered index.
Have an additional outside index as B-Tree. It’s not in table.
⚠️ Postgres doesn’t have primary index. All indexes are secondary index. (Non-clustered index)
Non-Clustered Index
- Located in separated memory section.
So, should jump to HEAP - One or more exists in a table.
- Store value and a pointer to actual row that holds data.
- The leaf node has only included columns.
- Just logical order, not organized physically.
- Keep Row ID (RID) in non-leaf level B+Tree.
- Composite key when used with unique constraints of the table act as non-clustered index.
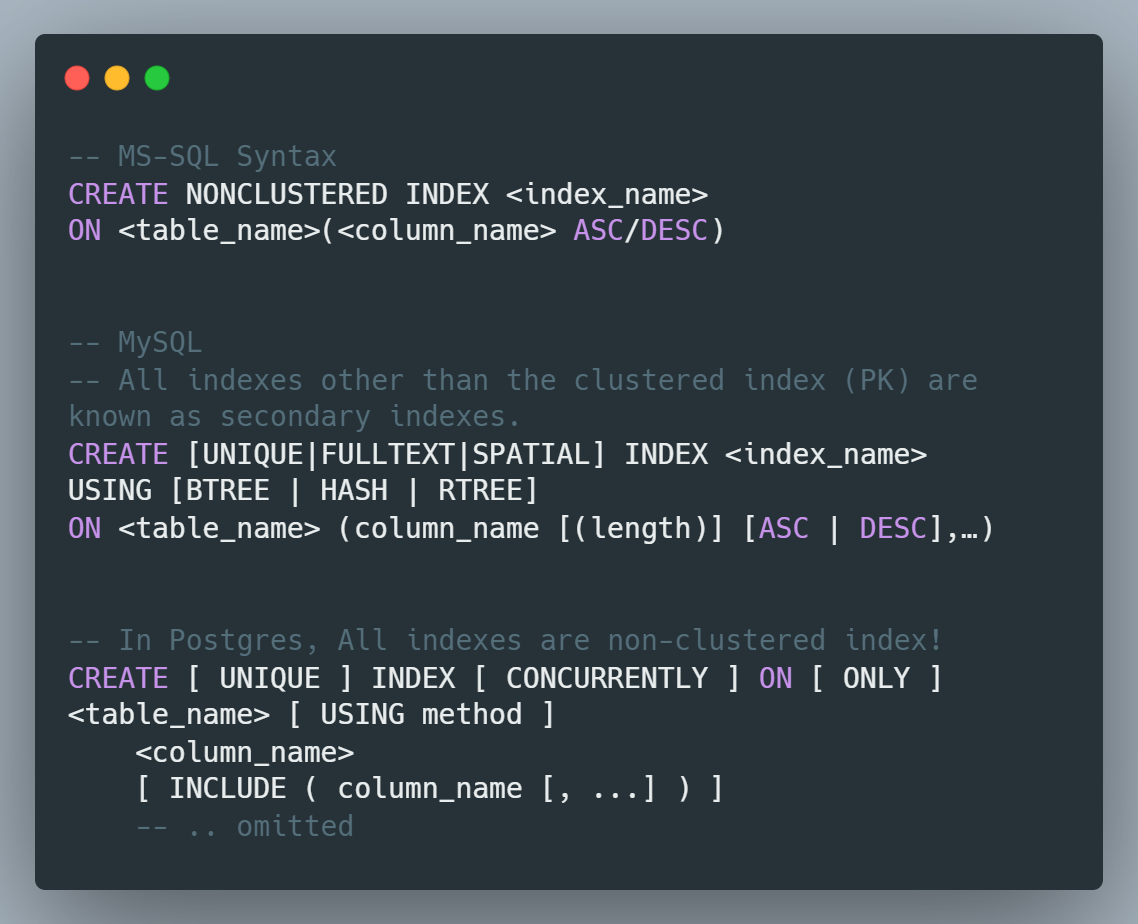
How to create non-clustered index in DBMS
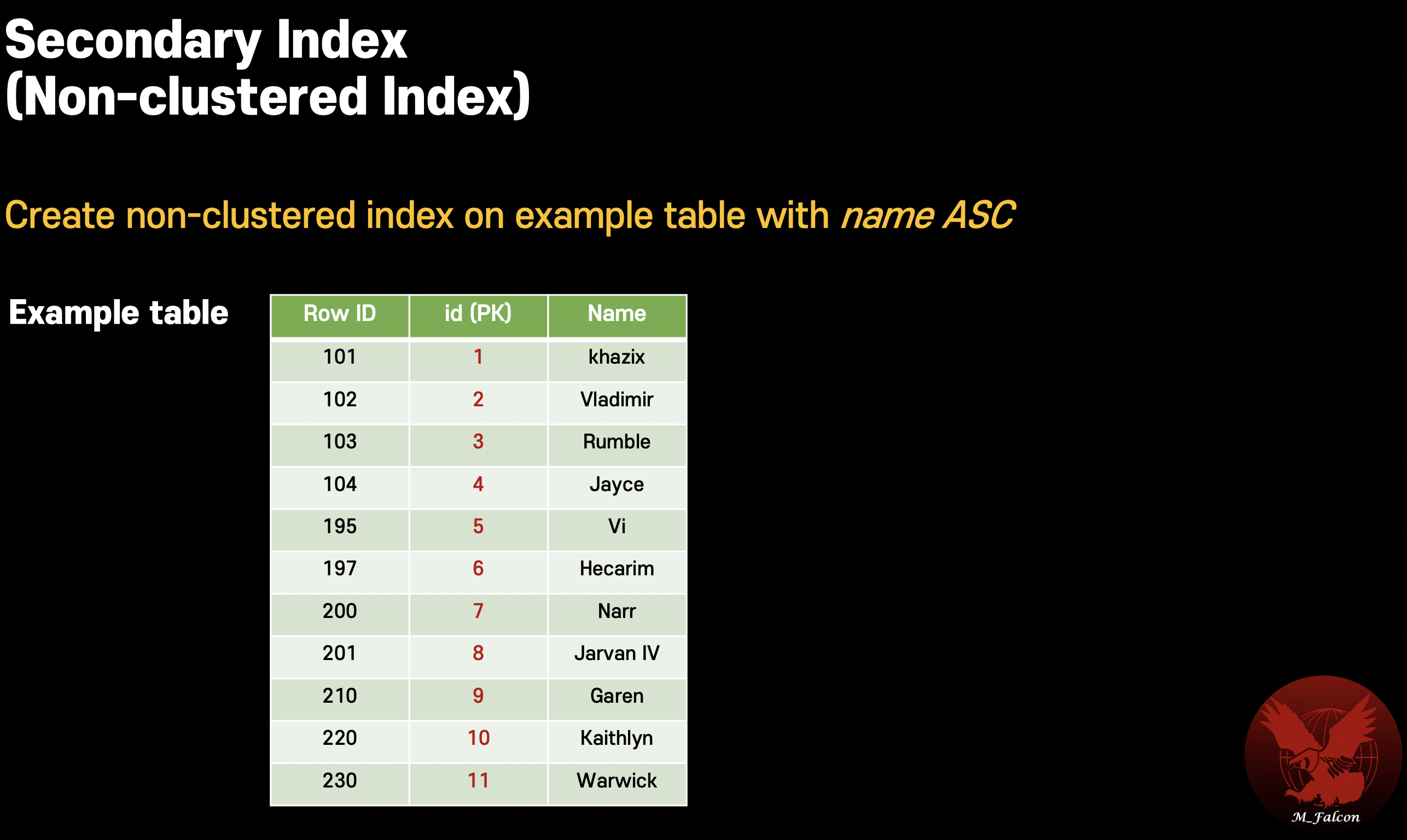
When to use non-clustered index architecture
- OLTP - character Query
- Selectivity almost close to 1
- Using covering index
Non-clustered index also sorted and stored in separate from heap space. - Massive aggregation function (by only index scan)
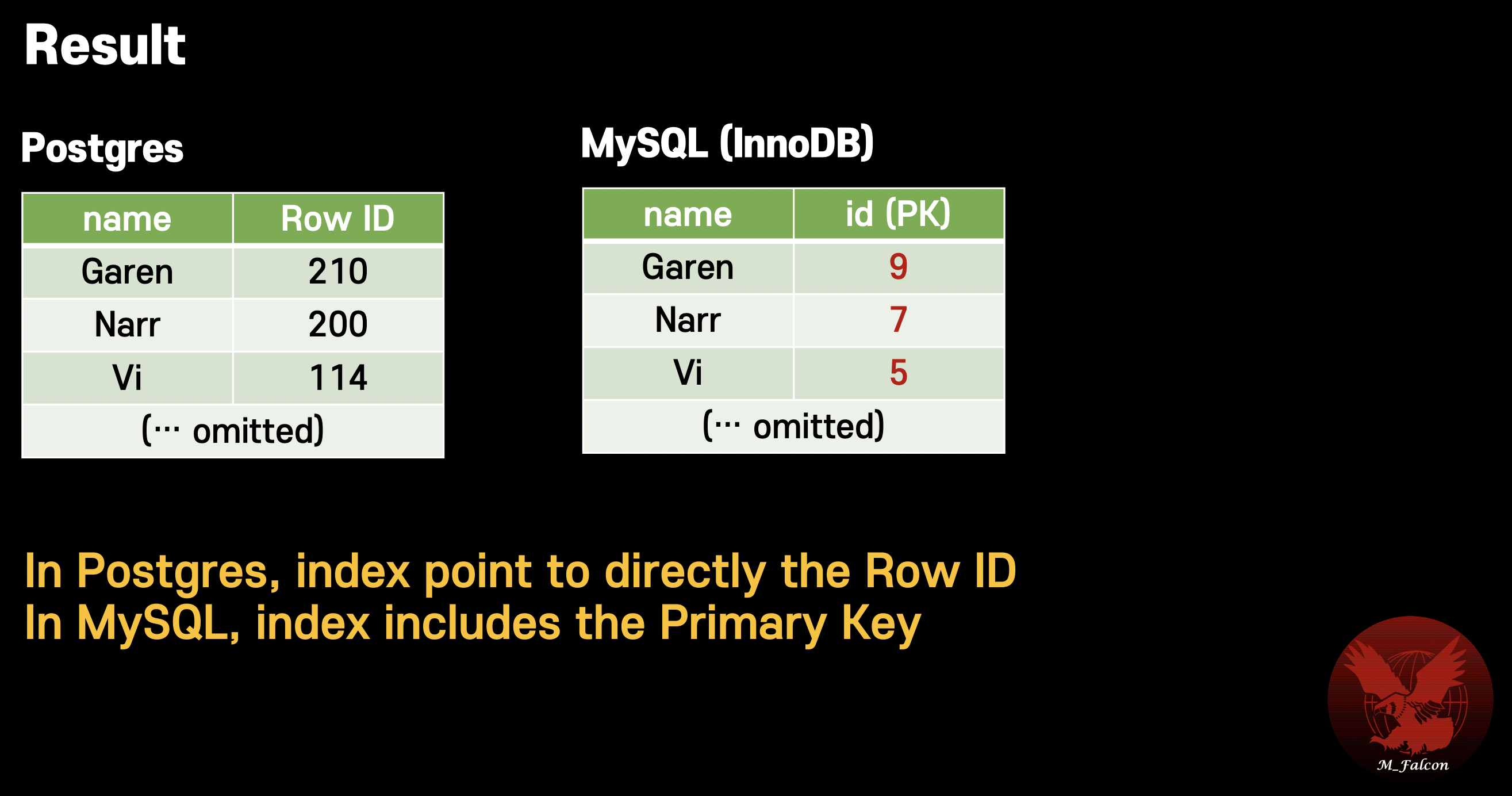
Secondary index in Postgres and MySQL
⚠️ Don’t use big primary key in MySQL using secondary index because it keeps primary key in secondary index
When create non-clustered index, automatically clustered index columns are added additionally.
Heap table
Table with no clustered index. (Only data page)
Clustered Index
When creating primary key(clustered index) is physically and logically sorted and with entire row data in data page (Heap).
Each page is connected with doubly linked list.
However, clustered index table doesn’t guarantee physical order of rows as time goes by.
Because INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE operations make a page split. Each age gets fragmented
On the other side, logical order of pages is sustainable with link.
Page split
In RDBMS, a table exists having auto increment Primary key 1, 3, 5, 7…
You insert primary key ‘2’ record on the table.
What happened?
- If page have empty space
=> insert the row in that page and update page offset.- If page doesn’t have empty space
=> split 50% data to a new page
Page split have impact on OLAP since there’s many empty page I/O.
However, doesn’t large impact on OLTP (low page I/O)
Why need index rebuild?
When rebuilding clustered index, fragments from page split are removed. After rebuilding, Pages and rows are organized physically , logically both.
Tips
Don’t create clustered index on running table. That work is so hard workload
When to use clustered index
- OLAP - character query
Performance 10 times than non-clustered index when you request query for massive data. - Massive join
- ORDER BY clause
- GROUP BY clause
In MySQL, MSSQL, clustered index is only Primary Key.
How to choice Primary key (Clustered index)
- Unique column
- Small key size
- Static column
Should not be updated, If not, page split occurs or re-balancing occurs
⚠️ In Index column, there’s only delete & insert solution for re-balancing
Not exists In-place update.
✅ This is auto_increment! But it’s not absolute solution.
