History of MongoDB Engine
MMAPV1 (~v2.x)
Map based data structure. So it has disadvantage about range-based query, concurrent update.
ID is consists fo Diskloc(collection data file name) + offset (bytes)
WiredTiger (~v5.1)
Support Document level locking so it’s able to update 2 document concurrently. Primary index _id and secondary indexes have been changed to point to recordId (a 64 bit integer)
instead of the Diskloc. It’s like a Postgres which point to rowID. Support compressed BSON. => Lower I/O => Lower Page => Getting more document -> Efficient Operation!
Current MongoDB (v5.2 ~)
Uses clustered index like MySQL. But it’s not enforced.
Secondary indexes are easy to bloat since _id is large (12 bytes). It no longer point to recordId. RecordId should point to _id which is 12 bytes.
Limit of Document Size
- Maximum: 16MB
- Minimum: 255KB
Index on MongoDB
Support Secondary and Primary index. It’s easy to bloat size of secondary index since ObjectId is 12 bytes.
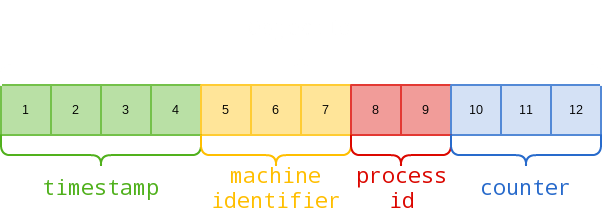
ObjectID (_id)
12 bytes PK.